Beijing-Jakarta partnership beyond trade
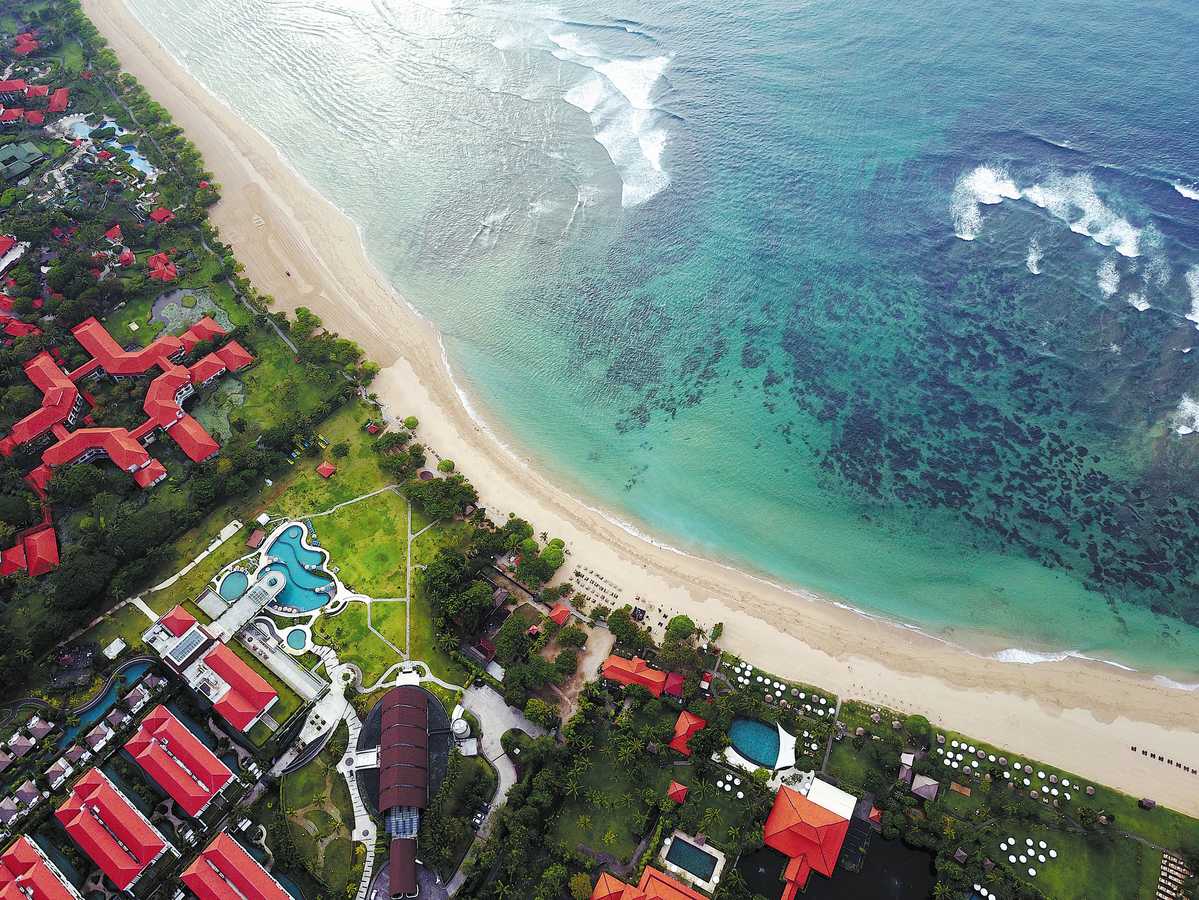


This year marks the 75th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations between China and Indonesia, which forged a partnership that has robustly grown over the decades. Central to this relationship is economic cooperation, particularly under the Belt and Road Initiative framework, which has substantially boosted bilateral trade and infrastructure development.
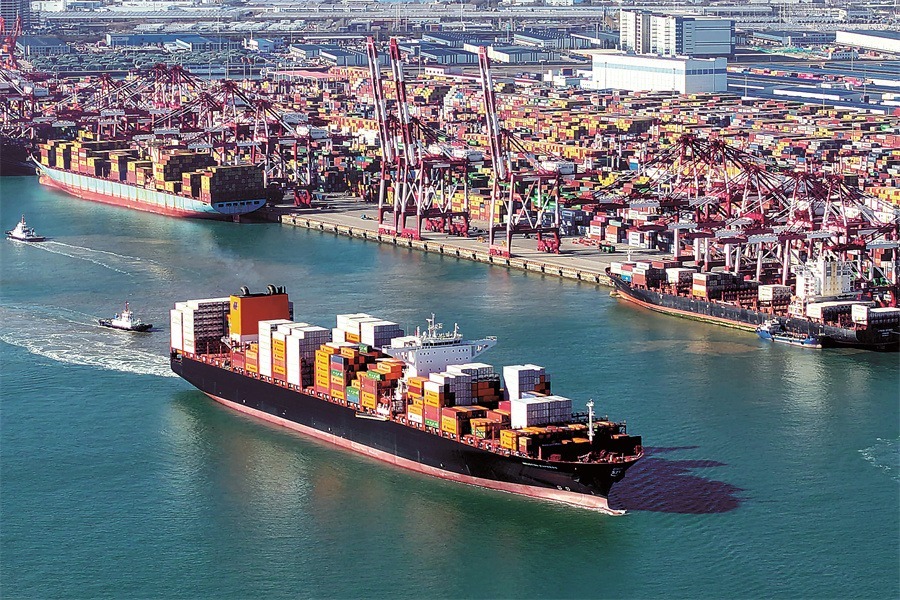
China has firmly established itself as Indonesia's largest trading partner. In 2022, bilateral trade reached about $133.64 billion, accounting for 25 percent of Indonesia's total trade, underscoring China's pivotal role in Indonesia's economic landscape. There was a slight decline of 4.4 percent in 2023, with trade totaling $127.82 billion, but in 2024, trade rebounded to $135.17 billion. The overall trend indicates deepening economic interdependence between the two countries.
Indonesia's exports to China mostly consist of resource-based commodities such as nickel-iron, thermal coal and liquefied petroleum gas, reflecting Indonesia's rich natural resource base and China's significant demand for raw materials. On the other hand, China exports high-value products such as machinery, electronics, and iron and steel products to Indonesia, meeting Indonesia's growing industrial and consumer needs. This complementary trade structure has facilitated balanced economic exchanges beneficial to both sides.
Infrastructure development remains a cornerstone of China-Indonesia economic cooperation under the Belt and Road framework. The Jakarta-Bandung High-Speed Rail stands out as a flagship project in Southeast Asia. Inaugurated in October 2023, this 142.3-kilometer-long railway has reduced travel time between Jakarta and Bandung from more three hours to about 40 minutes, reshaping inter-city connectivity and facilitating economic mobility. The project, executed by PT Kereta Cepat Indonesia-China, a joint venture between Indonesian state-owned enterprises and China Railway International, illustrates the significant benefits derived from international cooperation in large-scale infrastructure projects.
The successful completion of the Jakarta-Bandung HSR has spurred discussions on extending the high-speed rail network to Surabaya, which improve connectivity across Java, Indonesia's most populous and economically dynamic island. The proposed extension will reduce travel time between Jakarta and Surabaya from the current 8-13 hours to about 3.5 hours, promising substantial economic stimulation along this vital corridor.
Indonesia's rich nickel reserves have attracted significant Chinese investment, directly aligning with China's strategic initiative to secure essential minerals for its growing industries, especially in electric vehicles and batteries. A notable example of this cooperation is Indonesia Morowali Industrial Park in Central Sulawesi. Developed with extensive Chinese investment, IMIP has turned the region into a significant nickel processing hub, positioning Indonesia as a leading global nickel producer. This project has increased Indonesia's export revenue, created jobs and facilitated valuable technology transfers. But Indonesia is also seeking to diversify its investment sources in line with international trade norms. Initiatives are underway to attract foreign investment from different sources, reinforcing balanced and sustainable economic development.
Thanks to their shared commitment to global sustainability, China and Indonesia have deepened cooperation in renewable energy which, among other things, has given birth to the Cirata Floating Solar Power Plant in West Java, Southeast Asia's largest floating solar installation. Developed with Chinese technology and investment, the landmark project symbolizes the two sides' shared commitment to green energy solutions and is helping Jakarta realize its renewable energy goals.
Their collaboration in the financial sector is also expanding, led by the central banks of the two countries — the People's Bank of China and Bank Indonesia. The Indonesian central bank plays a pivotal role in enhancing bilateral financial cooperation through initiatives aimed at facilitating cross-border payments and settlements, promoting local currency transactions, and advancing financial technology and digital currencies.
This partnership holds special promise in the "two countries, twin parks" framework, providing a structured approach to simplify and secure cross-border financial flows. Further collaboration under the Digital Silk Road initiative is also expected to significantly boost payment system interoperability, digital financial inclusion, and technological innovation, strengthening the broader economic integration of the two sides.
Despite its many achievements, the China-Indonesia partnership faces some challenges. Certain projects should address people's concerns about environmental impacts and labor conditions, especially in nickel mining and processing. The challenges call for sustainable and socially responsible investment to mitigate negative the environmental impact and foster long-term stability and prosperity.
Geopolitically, Indonesia must continue to cautiously navigate complex international relations, balancing its strategic interests amid global competition between major powers. Indonesian President Prabowo Subianto's visits to China and the United States shortly after his inauguration in 2024 showed Indonesia's intention to maintain balanced global engagement between the two global powers, while safeguarding its strategic autonomy.
The China-Indonesia partnership is set to deepen further, driven by mutual interest, in emerging sectors such as the digital economy, healthcare and education. Regular dialogue, high-level diplomatic exchanges, and sustained commitment of both sides reflect their determination to jointly address future challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
As China and Indonesia commemorate 75 years of diplomatic relations, their cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative symbolizes a dynamic, evolving and resilient partnership.
The author is an assistant professor in the Faculty of Economics and Business at the Indonesian International Islamic University and a member of the advisory board at Reform Initiatives, Indonesia.
The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.