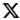Heavenly horse 'reins' again
Ancient bronze artwork discovered in 1978 symbolizes vigor of culture, Zhao Xu and Ma Jingna report.

This is not merely a bronze horse from nearly 2,000 years ago — it transcends the title of a masterpiece of art. For the Chinese today, it is a symbol of strength, an emblem of fortitude, a token of the vigor and verve that defines both its era and our own.
It is a galloping horse frozen in a moment of pure exhilaration, all four hooves off the ground and head tilted to one side in joyous abandon. Every detail — from the flared nostrils to the gaping mouth and wide, bulging eyes — speaks to the boundless energy coursing through the animal's veins in that fleeting moment.
As if the sense of speed were not yet fully captured, a bird appears beneath the horse's raised right hind hoof. Startled, it turns back in alarm — just as the unstoppable force of the horse overtakes it.
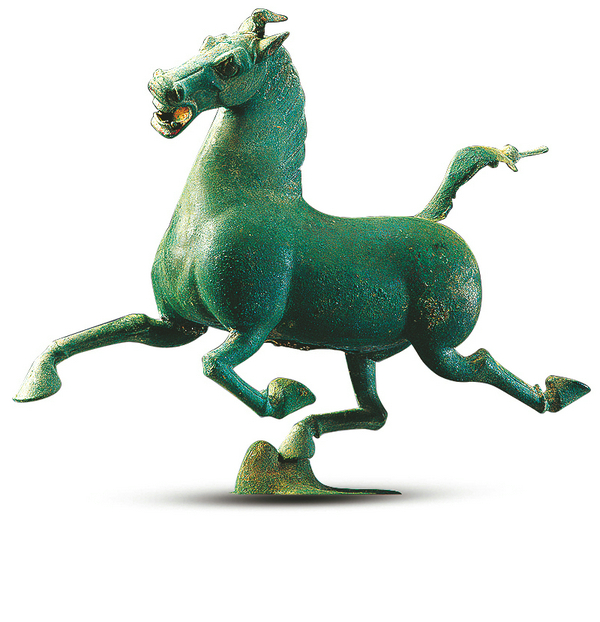

Since its discovery in 1978 in a Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220) tomb dated to around the late 2nd century, the bronze horse, standing at approximately 36 centimeters in height, has been regarded as the most prominent representation of the "heavenly horses" frequently mentioned in historical texts of the era. These horses, a breed native to the ancient Kingdom of Dayuan in present-day Uzbekistan, were prized for their exceptional build and stamina, making them ideal warhorses.
Emperor Wudi of the Han Dynasty, believing that smooth passage along the Hexi Corridor would help fill his stables with these remarkable creatures, desperately sought to acquire them.
That goal was eventually accomplished. The horse, currently on display at the provincial museum in Lanzhou, Gansu province, offers a fitting starting point for any traveler hoping to dive into that history.
Few may realize that although Lanzhou, as the provincial capital, is not technically part of the Hexi Corridor, it lies a mere 160 kilometers from Wushaoling, or Wushao Mountain, the eastern end of the corridor. In 121 BC, Huo Qubing, poised to become the dynasty's guardian god in his battle against the nomadic Xiongnu horsemen, entered the Hexi Corridor from here.